The core technology of this Repository of Glyco-Enzyme Expression Constructs is the generation of recombinant forms of the glycosylation enzymes in soluble forms when possible. Each of the glycosylation enzymes has a different strategy for its subcellular localication, including in many cases membrane anchoring sequences.
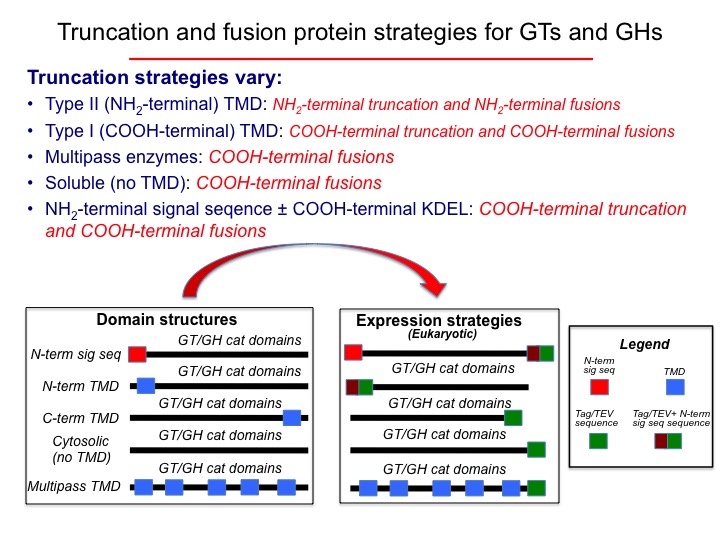
Summary of the glycosylation enzyme domain structures and topologies.
For each class of GT or GH sequence, truncation strategies were developed when possible to remove transmembrane segments to yield catalytic domains that could presumably be expressed in a soluble forms.
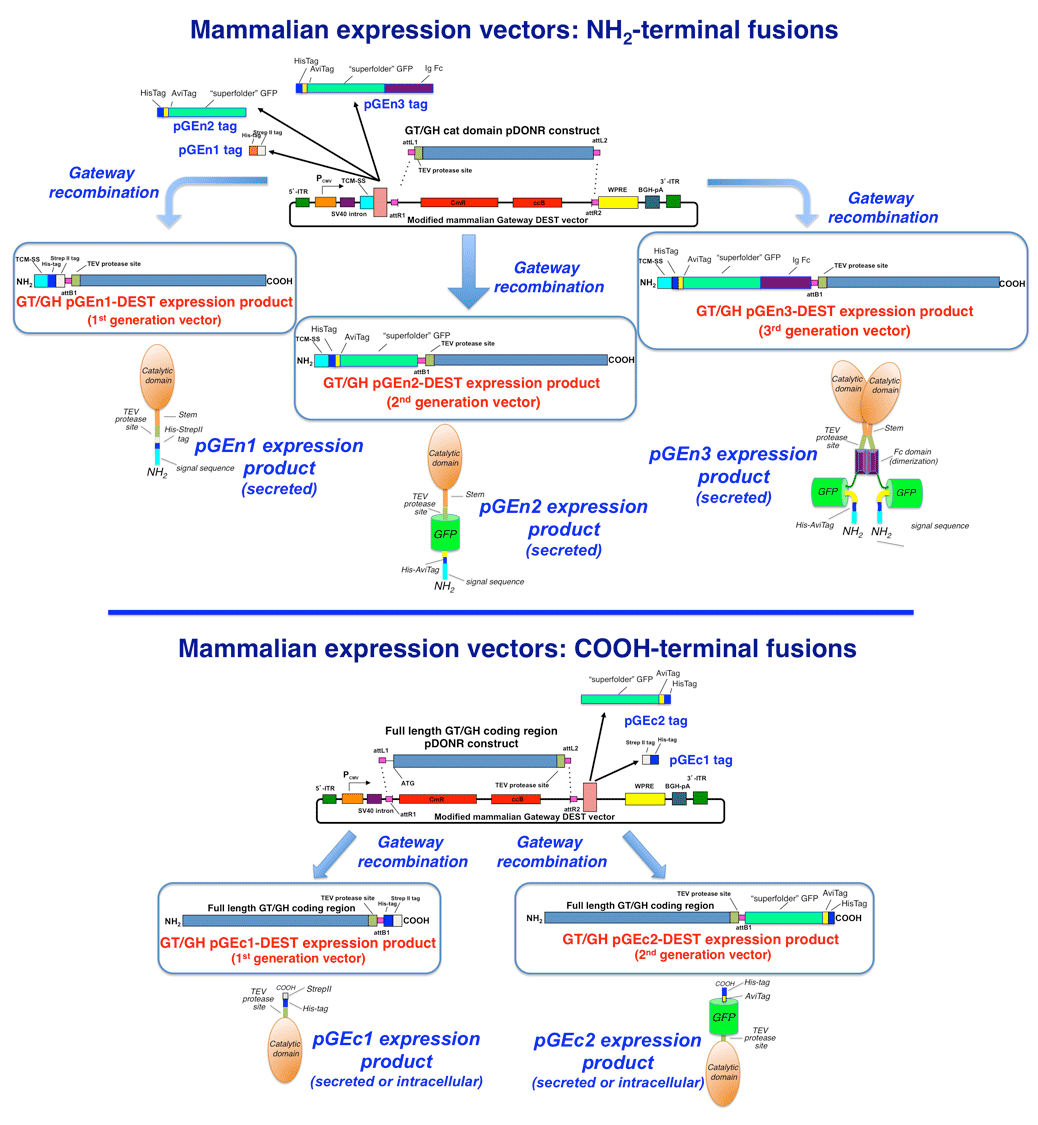
Summary of fusion protein strategies in mammalian and baculovirus vectors in the Repository.
For each class of GT or GH sequence, truncation strategies were developed when possible to remove transmembrane segments to result in a catalytic domain that could presumably be expressed in a soluble form.

Each class of expression constructs was generated as fusions to either the NH2-terminal or COOH-terminal epitope/affinity tag sequences for purification of the recombinant products. For proteins in the secretory pathway where NH2-terminal signal anchors were truncated, an NH2-terminal signal sequence was appended to provide entry into the secretory pathway. Finally, all constructs were generated with a TEV protease cleavage site proximal to the appended tag sequences so that the tags could be removed by TEV protease digestion following purification. An example of the three different tag strategies for the mammalian expression vectors are shown below.
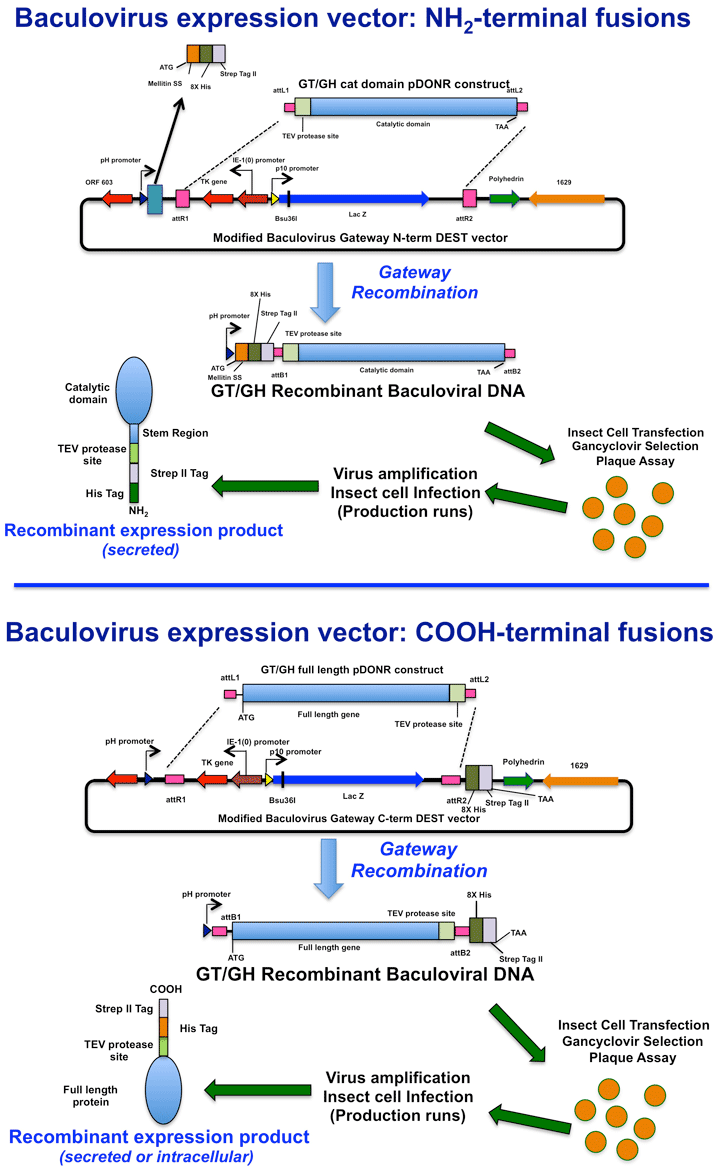
An equivalent diagram for the preparation of recombinant baculoviruses containing the coding regions for the tagged glycosylation enzyme constructs is shown below.
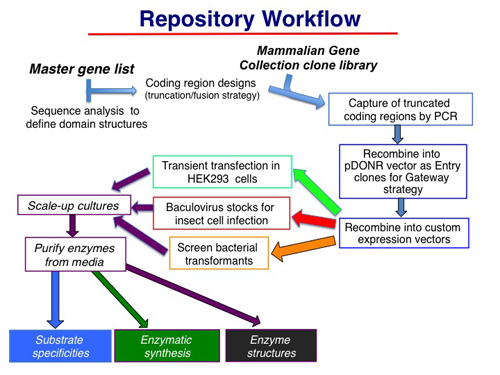
Thus, all protein coding regions were captured by PCR from templates in plasmids obtained from the Mammalian Gene Collection or by gene synthesis. In the process of amplifying the respective coding regions additional sequences were appended onto the amplimer products. In each instance, Gateway att recombination sites were appended distal to the coding region and TEV protease cleavage sites were incorporated into either the NH2-terminal or COOH-terminal extensions. The amplimer products were then captured in Gateway entry vectors (pDONR221) using the BP recombinase reaction. Entry clones were then recombined via LR recombinase reaction with mammalian, baculovirus, or bacterial destination vectors (see the expression vector collection HERE) to generate the library of espression constructs that comprise the repository. A workflow diagramfor construct preparation and analysis is shown below.